JavaScript字符串操作方法
字符串拼接方法
- concat()用于将一个或多个字符串拼接成一个新字符串
1 | let stringValue = "hello "; |
- 可以接收任意多个参数,因此可以一次性拼接多个字符串;
1 | let stringValue = "hello "; |
从字符串中提取子字符串的方法
- slice()、substr()和 substring();
- 这3个方法都返回调用它们的字符串的一个子字符串,而且都接收一或两个参数;
- 不会修改调用它们的字符串,而只会返回提取到的原始新字符串值;
| 方法 | 参数一 | 参数二 |
|---|---|---|
| slice() | 子字符串开始的位置 | 提取结束的位置 |
| substr() | 子字符串开始的位置 | 返回的子字符串数量 |
| substring() | 子字符串开始的位置 | 提取结束的位置 |
1 | let stringValue = "hello world"; |
- 当某个参数是负值时:
- slice()方法将所有负值参数都当成字符串长度加上负参数值;
- substr()方法将第一个负参数值当成字符串长度加上该值,将第二个负参数值转换为 0;
- substring()方法会将所有负参数值都转换为 0;
1 | let stringValue = "hello world"; |
字符串位置方法
- 有两个方法用于在字符串中定位子字符串:indexOf()和 lastIndexOf()
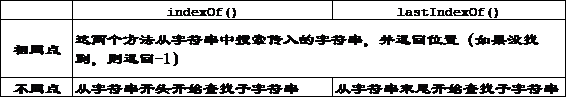
1 | let stringValue = "hello world"; |
- 这两个方法都可以接收可选的第二个参数,表示开始搜索的位置;
1 | let stringValue = "hello world"; |
字符串包含方法
- startsWith()、endsWith()和 includes()用于判断字符串中是否包含另一个字符串的方法
- startsWith()检查开始于索引 0 的匹配项
- endsWith()检查开始于索引(string.length - substring.length)的匹配项
- includes()检查整个字符串
1 | let message = "foobarbaz"; |
- startsWith()和 includes()方法接收可选的第二个参数,表示开始搜索的位置;
- 如果传入第二个参数,则意味着这两个方法会从指定位置向着字符串末尾搜索,忽略该位置之前的所有字符
- endsWith()方法接收可选的第二个参数,表示应该当作字符串末尾的位置。如果不提供这个参数,那么默认就是字符串长度。如果提供这个参数,那么就好像字符串只有那么多字符一样
1 | let message = "foobarbaz"; |
trim()方法
- 这个方法会创建字符串的一个副本,删除前、后所有空格符,再返回结果;
- trimLeft()和 trimRight()方法分别用于从字符串开始和末尾清理空格符;
1 | let stringValue = " hello world "; |
repeat() 方法
- 这个方法接收一个整数参数,表示要将字符串复制多少次,然后返回拼接所有副本后的结果;
1 | let stringValue = "na "; |
padStart() 和 padEnd() 方法
- padStart()和 padEnd()方法会复制字符串,如果小于指定长度,则在相应一边填充字符,直至满足长度条件;
- 这两个方法的第一个参数是长度,第二个参数是可选的填充字符串,默认为空格(U+0020);
1 | let stringValue = "foo"; |
- 可选的第二个参数并不限于一个字符;
- 如果提供了多个字符的字符串,则会将其拼接并截断以匹配
指定长度; - 如果长度小于或等于字符串长度,则会返回原始字符串;
1 | let stringValue = "foo"; |
字符串迭代与解构
- 字符串的原型上暴露了一个**@@iterator方法**,表示可以迭代字符串的每个字符;
1 | let message = "abc"; |
- 在 for-of 循环中可以通过这个迭代器按序访问每个字符
1 | for (const c of "abcde") { |
字符串大小写转换
- toLowerCase()、toLocaleLowerCase()、toUpperCase()和toLocaleUpperCase()
- toLowerCase()和toUpperCase()方法是原来就有的方法;
- toLocaleLowerCase()和 toLocaleUpperCase()方法旨在基于特定地区实现;
字符串模式匹配方法
- match()方法,这个方法本质上跟 RegExp 对象的 exec()方法相同;
- match()方法接收一个参数,可以是一个正则表达式字符串,也可以是一个 RegExp 对象;
1 | let text = "cat, bat, sat, fat"; |
- search()方法:唯一的参数与 match()方法一样:正则表达式字符串或 RegExp 对象;
- 这个方法返回模式第一个匹配的位置索引,如果没找到则返回-1。
- search()始终从字符串开头向后匹配模式
1 | let text = "cat, bat, sat, fat"; |
- replace()方法:接收两个参数,第一个参数可以是一个 RegExp 对象或一个字符串(这个字符串不会转换为正则表达式),第二个参数可以是一个字符串或一个函数
- 如果第一个参数是字符串,那么只会替换第一个子字符串。
- 要想替换所有子字符串,第一个参数必须为正则表达式并且带全局标记
1 | let text = "cat, bat, sat, fat"; |
- replace()的第二个参数可以是一个函数。
- 在只有一个匹配项时,这个函数会收到 3 个参数:与整个模式匹配的字符串、匹配项在字符串中的开始位置,以及整个字符串;
- 在有多个捕获组的情况下,每个匹配捕获组的字符串也会作为参数传给这个函数,但最后两个参数还是与整个模式匹配的开始位置和原始字符串;
- 这个函数应该返回一个字符串,表示应该把匹配项替换成什么;
1 | function htmlEscape(text) { |
localeCompare()方法
- 这个方法比较两个字符串,返回如下 3 个值中的一个;
- 如果按照字母表顺序,字符串应该排在字符串参数前头,则返回负值。(通常是-1,具体还要看与实际值相关的实现。)
- 如果字符串与字符串参数相等,则返回 0。
- 如果按照字母表顺序,字符串应该排在字符串参数后头,则返回正值。(通常是 1,具体还要看与实际值相关的实现。)
1 | let stringValue = "yellow"; |
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 姚永坤的小窝!
评论



