JavaScript——Math对象
- Math 对象上提供的计算要比直接在JavaScript实现的快得多,因为Math对象上的计算使用了JavaScript引擎中更高效的实现和处理器指令
Math对象属性

min() 和 max()方法
- min()和 max()方法用于确定一组数值中的最小值和最大值;
- 这两个方法都接收任意多个参数;
1 | let max = Math.max(3, 54, 32, 16); |
- 要知道数组中的最大值和最小值,可以像下面这样使用扩展操作符:
1 | let values = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]; |
舍入方法
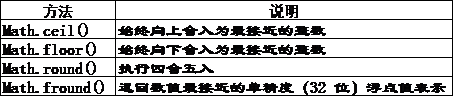
1 | console.log(Math.ceil(25.9)); // 26 |
random()方法
- Math.random()方法ᤄ回一个 0~1 范围内的随机数
- 从一组整数中随机选择一个数:
1 | number = Math.floor(Math.random() * total_number_of_choices + first_possible_value) |
1 | //从 1~10 范围内随机选择一个数 |
- 如果是为了加密而需要生成随机数,建议使用 window.crypto.getRandomValues()
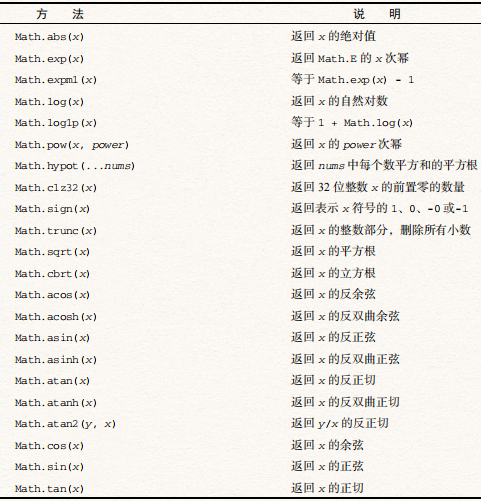
其他方法
本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 CC BY-NC-SA 4.0 许可协议。转载请注明来自 姚永坤的小窝!
评论



